Introduction: Arthroplasty, also known as joint replacement surgery, has become a transformative procedure in the field of orthopedic surgery. This surgical intervention involves replacing damaged or arthritic joints with artificial implants, providing relief from pain, restoring joint function, and improving overall quality of life. In this blog post, we will explore the benefits, procedure, and applications of arthroplasty, highlighting its remarkable impact on patients’ mobility and well-being.
- Understanding Arthroplasty: Arthroplasty is a surgical procedure that involves replacing a damaged or diseased joint, such as the hip, knee, or shoulder, with an artificial joint. The artificial joint, typically made of metal, plastic, or ceramic components, mimics the structure and function of a natural joint, allowing for improved mobility and pain relief.
- Advantages of Arthroplasty: a) Pain Relief: Arthroplasty effectively alleviates chronic joint pain caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or joint degeneration. b) Enhanced Mobility: By replacing damaged joints, arthroplasty restores joint function, enabling patients to regain mobility and engage in activities they were previously unable to perform. c) Improved Quality of Life: Arthroplasty can significantly enhance an individual’s overall quality of life by reducing pain, improving joint function, and restoring independence. d) Long-Term Durability: With advancements in implant technology and surgical techniques, arthroplasty implants are designed to be long-lasting, providing years of reliable performance.
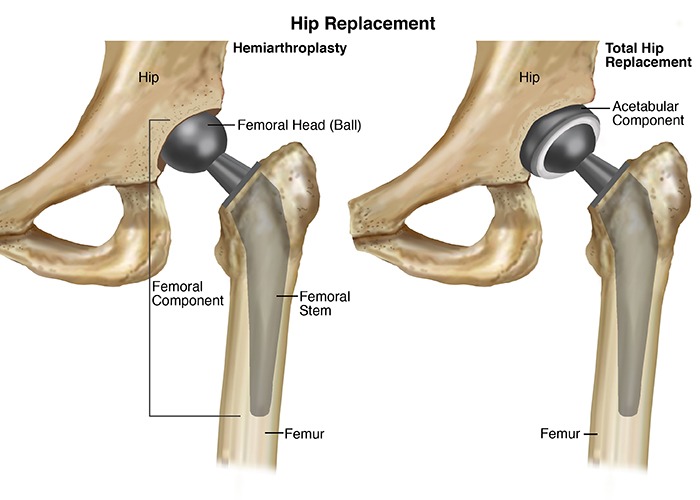
- Common Types of Arthroplasty: a) Hip Arthroplasty: This procedure involves replacing the hip joint with an artificial hip implant, relieving pain and restoring hip function. b) Knee Arthroplasty: Knee arthroplasty replaces damaged knee joint surfaces with artificial components, enabling improved knee movement and pain relief. c) Shoulder Arthroplasty: Shoulder arthroplasty involves replacing the damaged shoulder joint with artificial components, restoring shoulder mobility and alleviating pain. d) Other Joint Arthroplasty: Arthroplasty procedures can also be performed on other joints such as the elbow, wrist, and ankle, depending on the specific condition and patient needs.
- The Arthroplasty Procedure: Arthroplasty is typically performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon removes the damaged joint surfaces and prepares the bone to accommodate the artificial implant. The artificial joint components are then securely placed, and the surrounding tissues are carefully closed. The surgery is followed by a recovery period and postoperative rehabilitation to optimize joint function.
- Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation: After arthroplasty, patients undergo a rehabilitation program tailored to their specific joint and condition. Physical therapy and exercises help strengthen the joint, improve range of motion, and promote a successful recovery. Regular follow-up appointments with the orthopedic surgeon are essential to monitor the healing process and address any concerns.
Conclusion: Arthroplasty has revolutionized the treatment of joint-related conditions, offering pain relief, improved mobility, and enhanced quality of life for countless individuals. Through the replacement of damaged joints with artificial implants, arthroplasty has provided hope and restored independence to patients suffering from chronic joint pain. As technology and surgical techniques continue to advance, arthroplasty holds tremendous promise in further improving patient outcomes and transforming lives.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have concerns or questions about arthroplasty or any orthopedic procedure, consult a qualified healthcare professional.